Image analysis and understanding
The main issue addressed in this project-team is image analysis and understanding ie. extracting useful information in digital images and videos and transfer it into relevant description and prediction models. These models provide access to high level computer vision tasks as image recognition, object detection, semantic segmentation, pose estimation, emotion recognition. They rely on image processing or machine learning and particularly deep learning.
We are currently working on specific challenges raised by real data from other scientific fields or in connection with application fields:
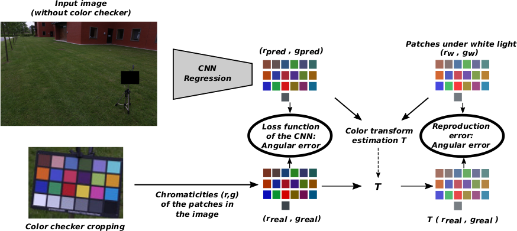
![]() Impact of lighting on color constancy – Color constancy is the ability of the human visual system to perceive consistent colors despite variations in lighting conditions. The aim here is to imitate this behavior with vision systems.
Impact of lighting on color constancy – Color constancy is the ability of the human visual system to perceive consistent colors despite variations in lighting conditions. The aim here is to imitate this behavior with vision systems.
A CNN model is trained to predict the chromaticities of the patches of a color checker without seeing this color checker. Then, the color correction matrix is estimated from the reference chromaticities under white light. Link to the paper].
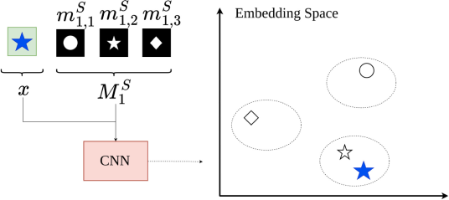
![]() Weakly supervised learning or learning using a priori knowledge – Learning representation spaces or invariant descriptors requires large volumes of annotated data. We propose methods for reducing the volume of annotated data by using self-supervision or a priori knowledge about the data.
Weakly supervised learning or learning using a priori knowledge – Learning representation spaces or invariant descriptors requires large volumes of annotated data. We propose methods for reducing the volume of annotated data by using self-supervision or a priori knowledge about the data.
The contrastive learning is leveraged to learn a latent space making images close to a binary mask seen as a proxy to a class. This strategy enhances the generalization properties of a neural network with a small number of annotated images. Link to the paper.
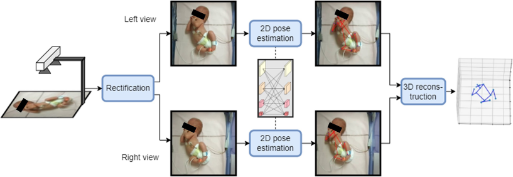
![]() Analysis of human expression and behavior – Our work aims to analyze facial expressions and body poses or movements, in particular to analyze emotions in “context-rich” scenes, or to analyze human behavior from videos.
Analysis of human expression and behavior – Our work aims to analyze facial expressions and body poses or movements, in particular to analyze emotions in “context-rich” scenes, or to analyze human behavior from videos.
We introduce the first stereoscopic system for infants’ 3D pose estimation, based on fine-tuning state-of-the-art 2D human pose estimation networks on a large, real, and manually annotated dataset of infants. Link to the paper.
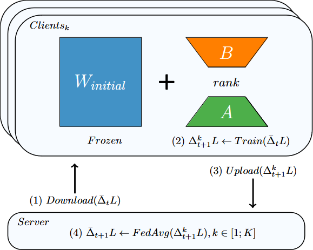
![]() Frugal and collaborative design for neural model implementation – We propose adapted and optimized methods for deploying models in cloud infrastructures, as well as in autonomous and non-autonomous Edge infrastructures. They are particularly based on distillation and federated learning.
Frugal and collaborative design for neural model implementation – We propose adapted and optimized methods for deploying models in cloud infrastructures, as well as in autonomous and non-autonomous Edge infrastructures. They are particularly based on distillation and federated learning.
FLoCoRa is a Low Rank Adaptation that allows to train small vision models in Federated Learning with low training complexity, reduction of communication between server and clients and small training memory requirement. Link to the paper.
We work in various scientific or application contexts such as: material characterization, biology, healthcare, human expression or behavior analysis, green technologies…